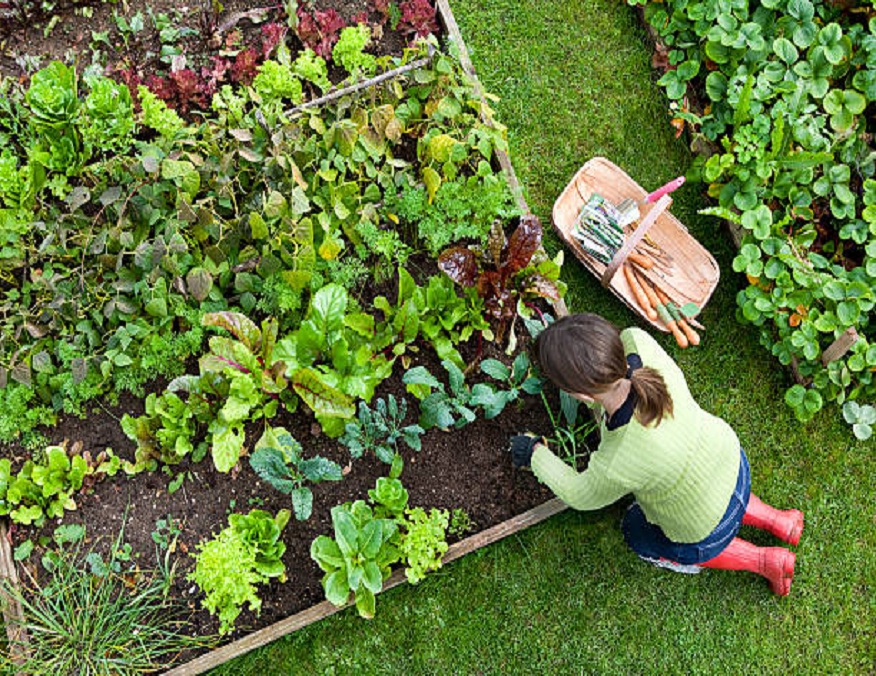
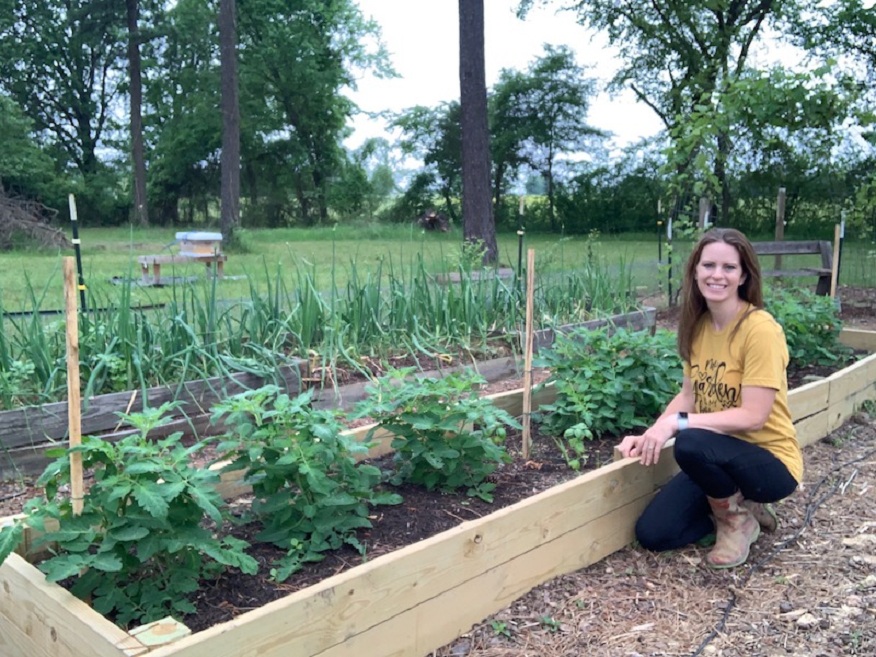
The raised garden can be defined as an above-ground garden, cultivated in height, in which the earth is retained by a tray of variable height .
A few decades ago, a vegetable garden was only conceived in large plots where a multitude of varieties of vegetables, aromatic plants and small fruits were lined up . We all remember the garden of a grandfather or a great-uncle, lovingly cultivated, where he spent most of his days, plowing, digging, hoeing, raking tirelessly. With the expansion of cities, cultivable land has shrunk, as has the time devoted to the garden.
the raised vegetable gardenAnd then, the vegetable garden entered the very heart of the cities via the development of the concept of vegetable garden imagined in 1976 by Mel Bartholomew, an American engineer.
Today, vegetable beds are no longer necessarily square, but the idea of the raised garden has made its way .
Practical, ergonomic, it allows you to grow a few vegetables, aromatic plants and strawberries on a small surface, almost anywhere. We tell you everything about these raised gardens and their advantages: how to make them? where and when to install them? What soil to put there and what vegetables to grow there?
A vegetable garden of various shapes
Directly inspired by the square vegetable garden which was originally structured in 16 small squares, the raised garden is less rigorous in its form and design.
It can be square, rectangular, round for those who want to be fancy, built as a staircase on several levels … the main thing being that the crop beds are raised above the ground. Going even further, the so-called keyhole garden or keyhole garden is also a raised garden with integrated compost. Also think about the very trendy and effective thick felt vegetable bed for growing your vegetables and flowers.
Ideal on rough ground
raised vegetable garden for difficult soil raised vegetable garden for difficult soilThus, vegetables, aromatics and small fruits gain height. This type of vegetable garden is particularly suitable for all those who have poor, dry, stony ground , too clayey therefore compact, too sandy therefore too draining, in short a thankless soil where any cultivation becomes difficult and often synonymous with failure.
With a raised vegetable garden, vegetable plants are offered a suitable, richer soil , most often retained by wooden planks, even wicker or hazel plessis, resistant and very aesthetic, or even dry stones, cinder blocks , concrete… The best and most practical to use is wood .
For many, cultivating a raised vegetable garden is an obligation in the face of too poor soil or too small an area to consider a garden in plots separated by paths.
However, the vegetable garden in height can also be designed for other reasons, perhaps less rational, but just as valid. Because making an above-ground vegetable garden has many advantages from a cultural, physical or practical point of view:
The earth is less low! Indeed , with a raised garden, you gain in working comfort since you have to bend down less . And your back is likely to thank you! The vegetable garden in height is indeed much more ergonomic. This is also one of the reasons why it is often installed to give the possibility to the elderly or people with reduced mobility to garden. Depending on the depth of your vegetable patch, you can garden sitting, kneeling or even standing. On the other hand, think carefully about its width which, in general, hardly exceeds 1.20 m in order to allow you to reach the cultures of the center at arm’s length.
The garden in height is isolated by a tray which acts as a barrier to creeping weeds and weeds which poison your life as a gardener. Admittedly, there will be a few, but fewer than in a conventional garden. That’s as many weeding and hoeing chores eliminated. Likewise, this bin is intended to be effective against moles or voles that like to wander around your plots.
Due to the configuration of the garden in height, the earth will warm up more quickly in spring thanks to the first rays of the sun. It is therefore possible to sow seeds there earlier than in the open ground. Similarly, the substrate is more airy, lighter because it is not subject to trampling and therefore more draining. Rainwater penetrates better because the soil is not subject to runoff. And the earth is maintained.
The raised vegetable garden can be installed anywhere , on ungrateful soil or a lawn but also on non-soil soil, for example in a courtyard or on a terrace, or even a balcony. In these last configurations, it will be necessary to install a tarp to contain the earth. Otherwise, it is not necessary on earthy ground. On the contrary.
The last advantage of the raised vegetable garden is aesthetic . If you take care of your container, these square vegetable gardens turn out to be very pretty, for example surrounded by pretty lawned paths where you can move around without difficulty. If you make or buy a wooden or plessis planter, your outdoor space gains in charm and authenticity. The other materials fit well into a contemporary exterior.
Raised vegetable patch and freestanding vegetable patch, two different uses
The vegetable garden on feet is by definition raised by feet which isolate it from the ground. We are indeed in an above-ground culture but the vegetable garden on feet could more easily be compared to a large planter, a bin or a large pot .
example of a vegetable gardenOn the other hand, it has a size advantage, it is precisely its size. It is indeed raised by 80 or 90 cm to be able to garden seated or even standing.